WSC Weekly 2025世界学者杯 the World Scholar's Cup

@WSC小学者们!Jerry喊你来看
WSC Weekly专栏啦!
2025年度主题:重燃未来
Reigniting the Future

全新主题火热上线
WSC Weekly专栏将精选最新话题内容
助力小学者准备世界学者杯!
让我们怀着
永恒的学术精神与信念
探索未来的无限可能吧!
即日起锁定每周WSC Weekly
上期回顾&Quiz答案揭晓
在2025年世界学者杯第8期WSC Weekly栏目中,我们与小学者认识了冻土这个“微生物冰箱”。在上期的趣味Quiz中,你是否找到了正确答案?现在就让我们一起来揭晓吧!
气候变暖会让远古时期的病毒复活吗?
Could global warming awaken ancient viruses?
第8期Quiz答案揭晓:
Which of the following is NOT a possible consequence of permafrost thaw? 以下哪项不是永久冻土融化可能造成的后果?
A. Release of greenhouse emission gases 释放温室气体
B. Mutation of human genes 人类基因突变
C. Release of radioactive waste 释放放射性废料
D. Discovery of extinct viruses 发现已灭绝的病毒
E. Evolution of modern species 现代物种的进化
正确答案:B
Key: B
2025年第9期
Weekly Intro
当你“开脑洞”时,你的大脑正上演一场精彩大戏,想象力不只是灵感闪现,而是神经元们活跃起来,大脑系统性运作的结果。本期 Weekly,一起揭开想象力的运行奥秘。
2025 No.9
当你“开脑洞”时,你的大脑发生了什么?
What happens in your brain when you imagine things?
想象力的秘密
想象力长期以来被视为人类独有的特质——它是故事创作、科技创新、共情能力乃至希望的源泉。无论是构想新发明还是描绘尚未存在的世界,想象力让我们得以突破现实的桎梏。但这种神秘的心智能力在大脑中究竟如何运作?当我们想象从未见过或经历的事物时,生物层面会发生什么?
Imagination has long been celebrated as a uniquely human trait—the root of storytelling, innovation, empathy, and even hope. From envisioning a new invention to picturing a world that doesn't yet exist, imagination is what allows us to move beyond the present. But what does this mysterious mental ability actually look like inside the brain? What happens on a biological level when we imagine something we've never seen or experienced?
脑海中的重构术
根据神经生物学的最新研究,想象力不仅仅是心灵的神秘馈赠,它是大脑高度协调活动的产物。研究的一个基础概念是将“表象”(imagery) 与“想象”(imagination)区分开来。表象是指对曾经经历过的事物进行心理重现——比如回忆一张面孔、一种声音或一个地方。而想象则更具创造性和开放性,它意味着在大脑中构建出全新的心理图像或概念,通常是通过将过去的体验元素以全新方式重新组合。两者密切相关,但想象力依赖于更复杂的信息重组过程。
According to recent research in neurobiology, imagination is not just a mystical gift of the mind—it's the result of highly coordinated brain activity. A foundational concept is the distinction between imagery and imagination. Imagery refers to mentally recreating experiences we've had before—like remembering a face, a sound, or a place. Imagination, by contrast, is more creative and expansive. It involves forming entirely new mental images or ideas, often by combining elements of past experiences in novel ways. Both processes are deeply connected, but imagination depends on a more complex reorganization of information in the brain.
神经“征用”
这种重组能力得益于一种被称为神经重部署(neural redeployment)或扩展适应(exaptation)的现象,即某些最初进化出来用于特定功能的脑区,被重新“征用”来执行其他功能。例如,当你想象自己攀登高山时,你的大脑会激活与真实身体运动相关的区域,比如前运动皮层和顶叶皮层。在你观察别人运动时,这些区域也会活跃起来,这得益于镜像神经元(mirror neurons) ——它们会在你大脑中“模拟”他人的动作。神经科学家推测,这些神经系统可能在进化过程中被“借用”来服务于对行为、情感和经验的想象性模拟。
This reorganization is made possible by a phenomenon known as neural redeployment, or exaptation. This is when brain structures originally evolved for one purpose are reused for another. For example, when you imagine yourself climbing a mountain, your brain activates many of the same regions involved in actual physical movement—such as the premotor cortex and parietal lobe. These regions are also active when you simply observe someone else moving, thanks to mirror neurons, which "mirror" the actions of others in your own brain. Neuroscientists suggest that these systems may have been co-opted by evolution to serve the imaginative simulation of actions, emotions, and experiences.

“内心世界”舞台
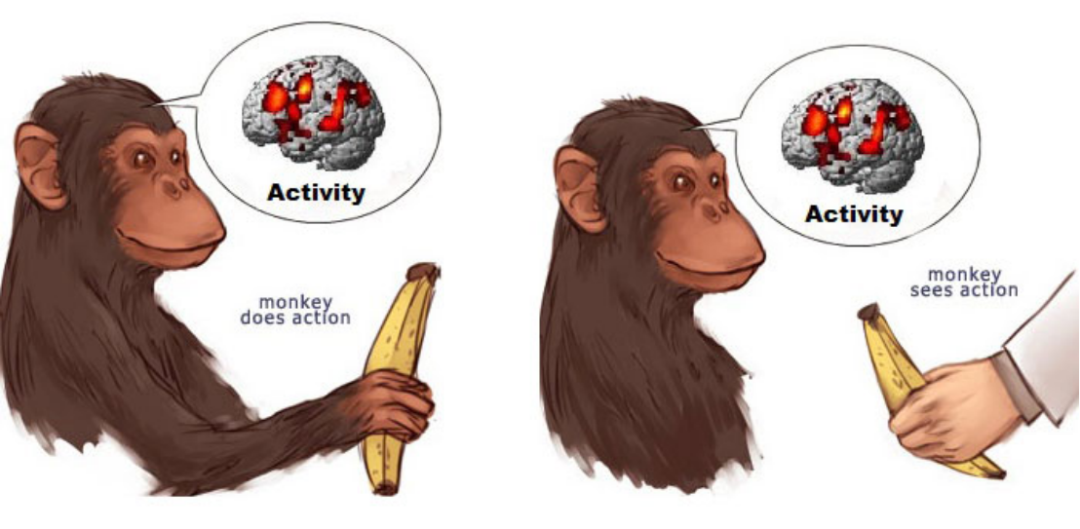
人类想象力之所以特别强大,在于大脑能在多个系统之间自由组合和重塑信息。这在很大程度上得益于一个被称为默认模式网络(Default Mode Network,简称DMN)的大脑系统。DMN是在我们不进行专注任务时激活的一组互联脑区,它在我们白日梦、反思自我、想象未来场景或构建虚拟现实时发挥关键作用。DMN调动记忆、情绪、感知,甚至社会认知等要素,编织出丰富的内在叙事。可以说,DMN就是我们“内心世界”的舞台。
What makes human imagination especially powerful is the brain's ability to combine and reshape information across many systems. This is supported by the default mode network (DMN)—a group of interconnected brain regions that becomes active when we're not engaged in focused tasks. The DMN lights up when we daydream, reflect on our identity, imagine future scenarios, or mentally construct alternate realities. It draws on memory, emotion, perception, and even social cognition to build rich, internal narratives. In essence, the DMN is the stage where our inner world comes alive.
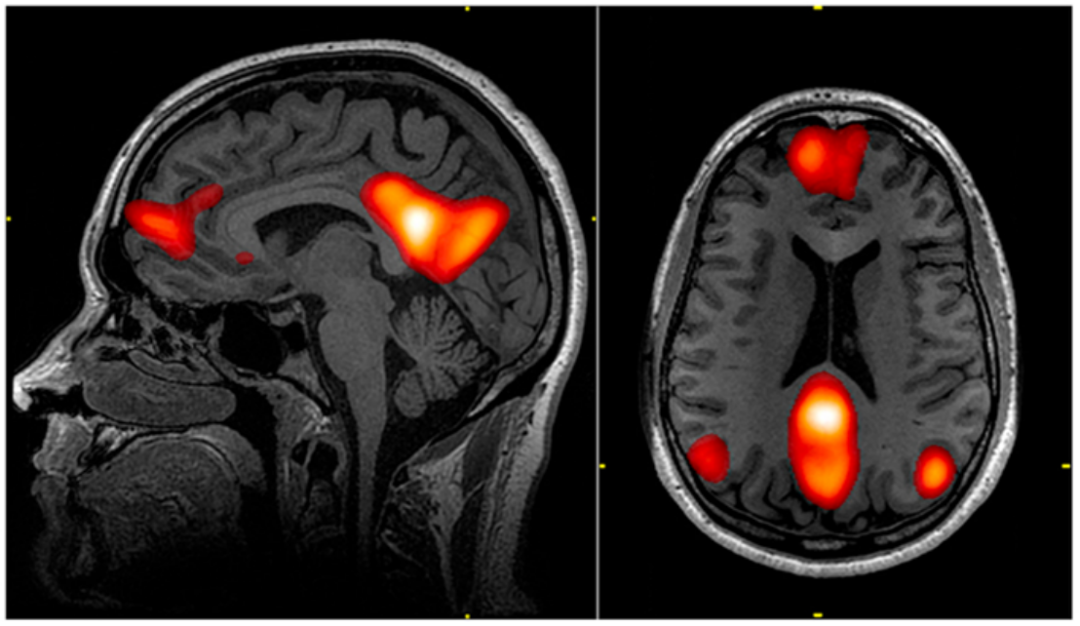
共情和想象力的桥梁
另一个重要的神经系统是冯·埃科诺莫神经元(Von Economo neurons, VENs)。这是一种大型的纺锤状神经元,存在于与自我意识、情绪及复杂决策相关的大脑区域中。科学家认为,VENs有助于快速整合情感与社交信息,在人类想象自己扮演不同角色、站在他人视角思考问题的能力中发挥着重要作用。有趣的是,VENs在人类大脑中的数量远多于其他物种,也被认为是共情能力和高级想象力的重要基础。
Another key player is the Von Economo neurons (VENs)—large, spindle-shaped neurons found in parts of the brain responsible for self-awareness, emotion, and complex decision-making. These neurons are thought to help integrate emotional and social information quickly and may play a central role in our ability to imagine ourselves in different roles or perspectives. Interestingly, VENs are found in much higher numbers in humans than in other species and are believed to be crucial for empathy and higher-level imaginative thought.
千变万化的神经网
此外,大脑还通过所谓的功能模块(functional modules)来支持想象力。这些神经元网络可以根据任务的不同快速重组。它们之间通过两种方式传递信息:一种是“布线式”直接连接,另一种是通过脑液中弥散的“体积式”传播。由星形胶质细胞(astrocytes)和细胞外基质构成的支持系统调节这种传播,从而实现大脑区域之间灵活而高效的沟通。这个动态系统并非依靠固定架构运作,而是通过神经科学家所称的"交互主导动态机制(interaction-dominant dynamics)"运行——微小的系统局部变化即可引发功能性剧变。这使得有限神经元件能产生近乎无限的组合方式,解释了个体想象力何以既天马行空又独具特色:每个大脑都在调用独特的记忆、情感与视角创造新知。
The brain's structure also supports imagination through functional modules—networks of neurons that can be rapidly reassembled into different configurations depending on the task. These modules communicate via both wiring transmission (direct connections) and volume transmission (signals diffusing through brain fluids). Support cells called astrocytes and the extracellular matrix help regulate these transmissions, allowing for fluid, adaptive communication between brain regions. Importantly, this dynamic system does not operate through a rigid architecture. Instead, it functions through what neuroscientists call interaction-dominant dynamics—a flexible, ever-changing process where small changes in one part of the system can lead to large shifts in function. This allows the brain to use a limited number of neural components in a nearly infinite number of ways. It's why imagination can be both wildly creative and deeply personal: every individual's brain draws on different memories, emotions, and perspectives to generate new ideas.
Weekly关键词 Key Words
►imagination 想象力
►mental imagery 心理表象
►exaptation 扩展适应
►Default Mode Network (DMN)默认模式网络
►Von Economo neurons (VENs)冯·埃科诺莫神经元
所属话题
# The Generative Area: A Mind for Imagination
相关阅读
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3662866/pdf/fpsyg-04-00296.pdf
Weekly FUN Quiz
相信现在你已经对“发挥想象时的大脑活动”有了一定的了解啦!那就快来参与本期Weekly FUN Quiz👇,告诉老师你的答案吧!
Quiz
According to neuroscientists, imagining ourselves doing extreme sports can stimulate the same regions involved in actual physical movement, even if we never actually did such sports. This phenomenon is mainly related to which of the following mechanisms?
根据神经科学家的研究,我们想象自己在做极限运动时,会刺激参与实际身体运动的相同区域,即使我们从未真正做过此类运动。这种现象主要与以下哪种机制有关的?
A. Exaptation 扩展适应
B. Von Economo neurons 冯·埃科诺莫神经元
C. Default Mode Network 默认模式网络
D. Functional modules 功能模块
E. Interaction-dominant dynamics 交互主导动态机制